

The NTRs are regulated by Ran it mediates the association of the NTRs with the cargo and provides the energy which drive the transport across the membrane. Collectively, the system of transport is comprised of the protein cargo, nuclear transport receptors (NTRs) such as importins and exportins, and the small GTPase Ran. Molecules >40 kDa each have a specific means of transportation across the nuclear envelope.
Molecules smaller than ∼40 kDa can pass freely across the nuclear envelope and do not require passage through the NPC. They form aqueous channels that allow the selective movement of proteins, mRNA, tRNA, ribosome subunits and viruses in a bidirectional manner. They sit at the point at which the inner nuclear membrane fuses with the outer nuclear membrane. Nuclear pores are large protein complexes that form openings in the nuclear membrane. There are also other structural proteins in the nucleoskeleton which impact the spatial organization of lamin proteins and other mechanical properties, such as resilience in response to stretch. At the nuclear envelope, the A and C type laminins provide a stiffness to the otherwise unstructured nucleus, whilst simultaneously supporting DNA processing events such as chromatin remodeling during replication.ī-type laminins provide support the processes of transcription and cellular signaling. It forms an elastic structure near the nuclear periphery and affords a viscoelastic property to the nucleus. It is made up of intermediate V type filaments composed of lamin proteins. This is a network that provides support to the whole nucleus. Intermediate filaments form a network the nuclear lamina whilst other other inner nuclear membrane proteins mediate the interactions of the envelope with chromatin. The outer nuclear membrane is continuous with the rough endoplasmic reticulum. The nuclear envelope itself has both an inner and outer nuclear lipid membranes.

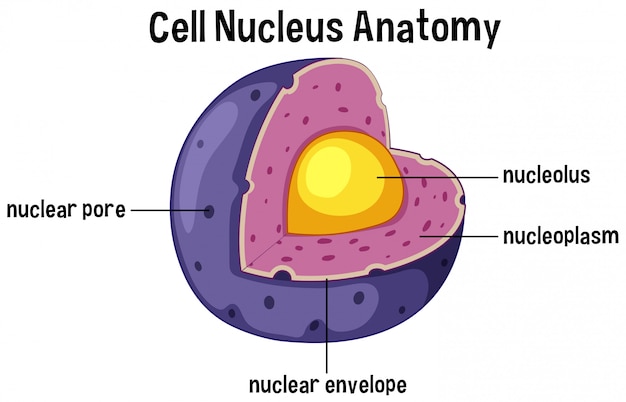
Additionally, it functions in nuclear processes such as DNA replication, particularly in the regulation of transcription factors. This maintains the shape of the nucleus, spaces the nuclear pore complexes and organizes heterochromatin, the condensed region of DNA of nucleus. The nuclear skeletal network (karyoskeleton) that results serves as an anchor for chromatin. These first form dimers, and subsequently orientate in a head-to-tail fashion to produce filaments. The fibrillar nature of the lamina arises from the building blocks of the lamina the laminin proteins. It is highly proteinaceous and is fibrillar in appearance. The Nuclear Lamina is a structure that is located near the inner nuclear membrane. These subcompartments together form the nucleoskeleton, and include the following:Ĭell and Nucleus, Image Copyright: sanjayart / Shutterstock Nuclear Membrane (nuclear envelope) These facilitate the various nuclear processes, particularly gene expression. The mechanical support and functional organization of the nucleus is contributed by several nuclear subcompartments, or nuclear bodies. Additionally, the nucleus dynamically interacts with the surrounding cytoskeleton. The nucleus is mechanically stable, possessing the ability to resist deformation. The nucleus contains approximately 2m of DNA which is enmeshed by the nuclear envelope, a crosslinked network of proteins and membranes. The effect of these processes extends to affecting cellular metabolism and growth. These processes include transcription, replication, splicing and ribosome biogenesis. The cell nucleus is the site of many important biological functions of the eukaryotic cell.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
